CE 433 2023 Spring
Report 5 Sequential
Circuit
Name: Vann Montoya
Email:
bvmontoya@fortlewis.edu
Sequential
Circuit
Introduction
Materials and Methods
gVim
Vivado
Results
Tasks
1. In Section 1, don't look at the logic equations
provided to you. From the state table, find the logic equations for
q1(n+1) and y and draw the sequential circuit for q1(n+1) and y. (10
points)
From the state table, we can trace each of the inputs for q2[n+1],
q1[n+1] and y.
Here's the traced state table:
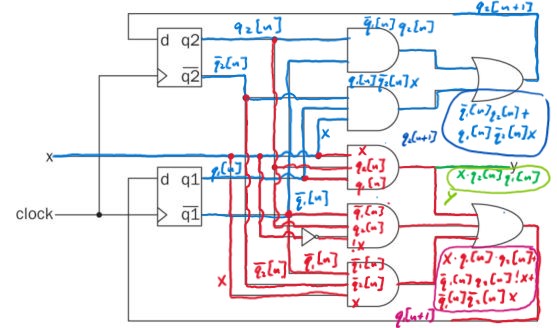
Figure 1: State table with
traced logic for q2[n+1], q1[n+1], and y.
From the diagram we see that:
q2[n+1] = q1[n] q2[n] + x q1[n] q2[n]
q1[n+1] = x q1[n] q2[n] + !x q1[n] q2[n] + x q1[n] q2[n]
y = x q1[n] q2[n]
2. Repeat the work in Section 3. Use two
methods, the given one and the behavioral one. Show simulation results.
(15 points)
Here's the code for Sequence Detector module and test bench:
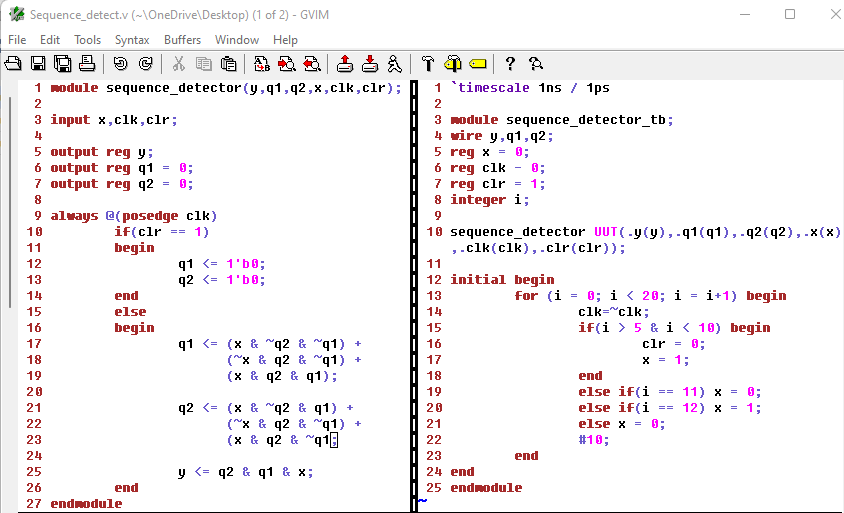
Figure 2: Code for the Sequence Detector module and test bench.
Here are the results from the simulation:
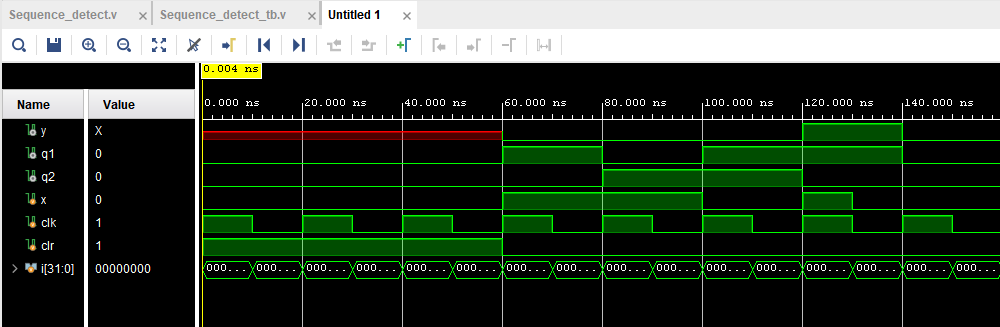
Figure 3: Simulation results for the Sequence Detector.
3. Similar to the sequence detector in Section 3, change the sequence
to be detected to 1011, design the state diagram, draw the truth table,
find the logic equations, and design the verilog module and testbench
to verify the logic. (15 points)
In order to update the simulation to accept 1011, we need to make a new state diagram.
Here's the new state diagram for 1011:
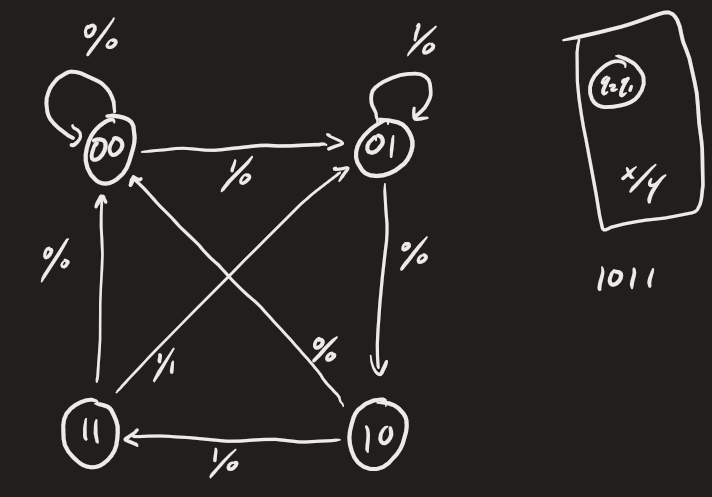
Figure 4: State diagram for 1011 input.
This gives a new truth table:
|
Present State
|
Input
|
Next State
|
Output
|
|
q2[n]
|
q1[n]
|
x
|
q2[n+1]
|
q1[n+1]
|
Y
|
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
0
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
0
|
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
0
|
|
1
|
1
|
1
|
0
|
1
|
1
|
Table 1: Truth Table for 1011 sequence detector.
Which gives the following logic:
q2' = q2 q1 x + q2 q1 x
q1' = q2 q1 x + q2 q1 x + q1 x
y = q2 q1 x
Here's the code for the updated sequence detector and test bench:
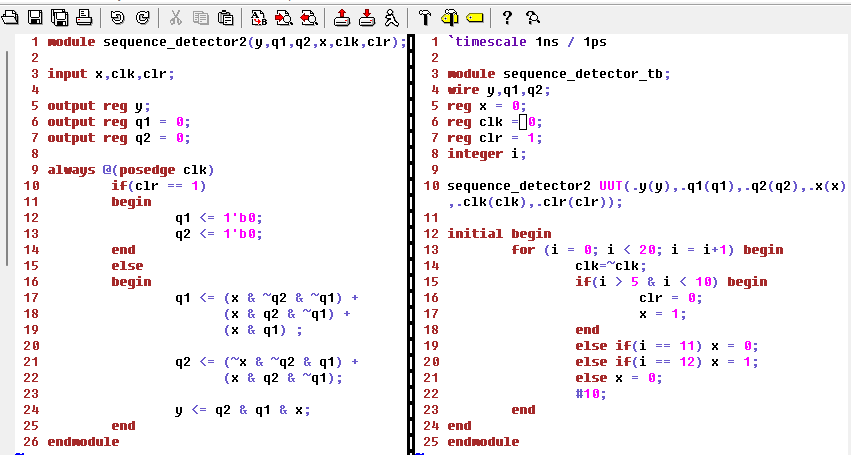
Figure 5: Code for the updated sequence detector and test bench.
Here are results from the simulation:
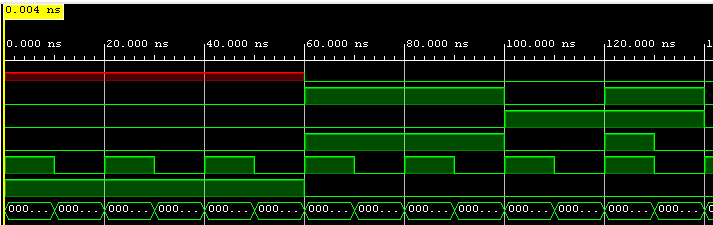
Figure 6: Results from the 1011 sequence results simulation.
4. Simulate the four types of shift registers in Section 5. (20 points)
SISO:
Here's the code for the SISO module and test bench:
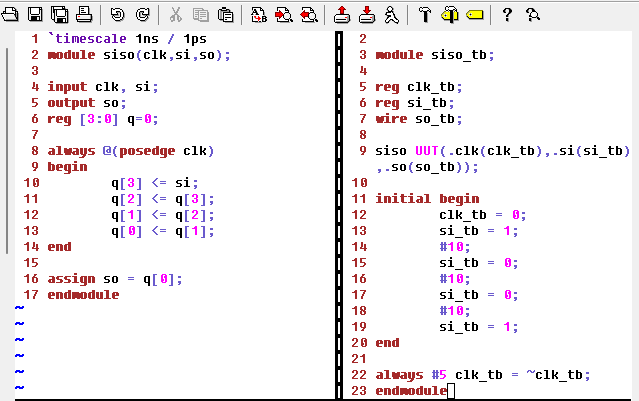
Figure 7: Code for the SISO module and test bench.
Here are the results from the simulation:
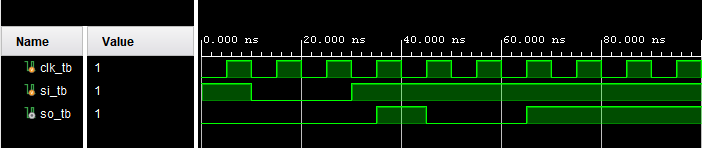
Figure 8: Results from the SISO simulation.
SIPO:
Here's the code for SIPO module and test bench:
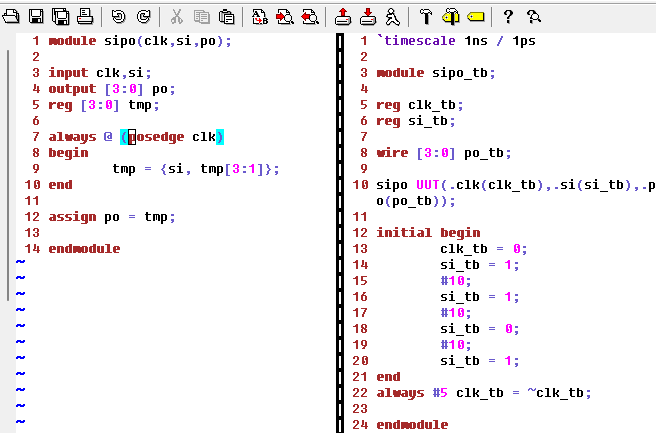
Figure 9: Code for the SIPO module and test bench.
Here are results from the SIPO simulation:
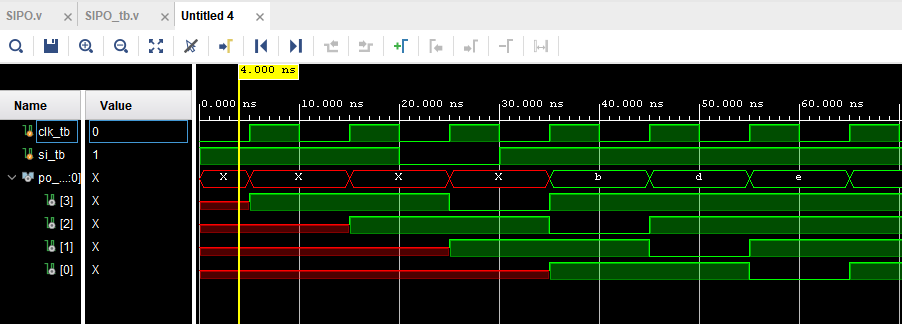
Figure 10: SIPO simulation results.
PISO:
Here's the code for the PISO module and test bench:
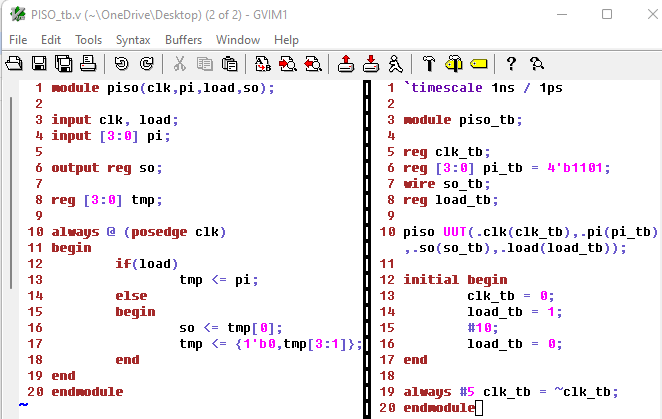
Figure 11: Code for the PISO module and test bench.
Here are the results from the PISO simulation:
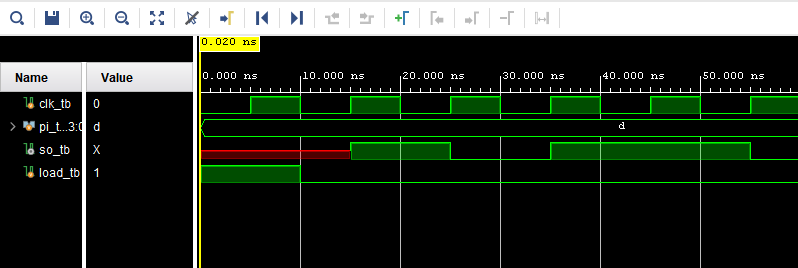
Figure 12: Results from the PISO simulation.
PIPO:
Here's the code for the PIPO module and test bench:
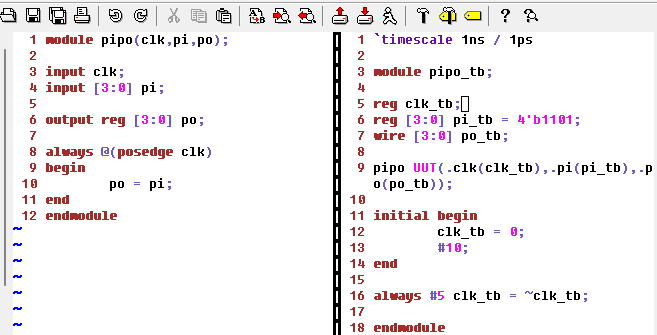
Figure 13: Code for the PIPO module and test bench.
Here are the results from the PIPO simulation:
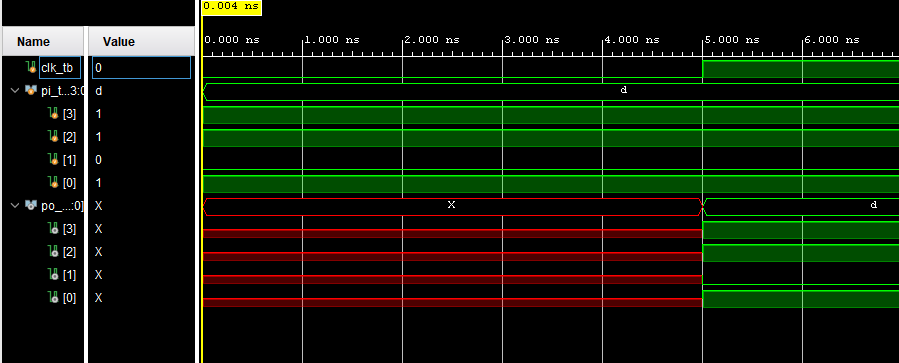
Figure 14: Simulation results from the PIPO module.
5. Build a counter module and show the simulation results. (20 points)
6. Find the logic equation of the following circuit and implement it in
verilog. Show the simulation results. (20 points)













